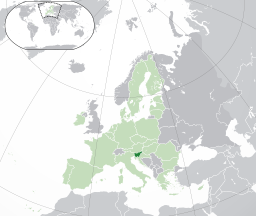
CFI Data on Slovenia
The light green area is the rest of the European Union
Slovenia was the 81st largest economy in the world by nominal GDP in 2018. Its GDP per capita was $26,234 USD. It has a highly educated workforce, well-developed infrastructure, and is strategically located between Western Europe and the Balkans. It was ranked 13th in the World Bank's Human Capital Index and 12th in the Economic Complexity Index in 2017. It is a member of the EU and OECD. Services was the largest economic sector in 2018 (56.3 percent of GDP), followed by manufacturing (20.1 percent), and agriculture (1.9 percent). In 2017, the largest export sectors were services (20.2 percent), chemicals (15.84 percent), vehicles (14.15), machinery (10.92 percent), and electronics (9.49 percent). The largest individual exports were cars (8.92 percent), ICT services (7.2 percent), travel and tourism (6.79 percent), packaged medicaments (6.4 percent), and transport services (5.8 percent). Its largest export partners were Germany (19.72 percent), Italy (10.3 percent), Croatia (7.87 percent), Austria (7.34 percent), and France (5.31 percent). The largest goods imports were cars (6.4 percent), refined petroleum (4.2 percent), parts of motor vehicles (3.6 percent), and packaged medicaments (2.6 percent). Industrialisation began slowly in the early 1800s and was spurred by the introduction of railway lines from the mid -1850s. In 1918 with the collapse of the Austro-Hungarian empire, Slovenia joined Yugoslavia but enjoyed little autonomy. After Yugoslavia broke with the Soviet Union in 1948, Slovenia and the other socialist republics within Yugoslavia were given increasing economic autonomy within a mixed market and socialist economy. In 1991, Slovenia declared independence. High inflation and the loss of the Yugoslav market was quickly overcome by tight monetary policy, sound fiscal policy, the introduction of its own currency, new export markets, and the expansion of the services sector. The reform process then proceeded gradually but was given new impetus by the EU accession process. These reforms and increased FDI led to increased growth. The global financial crisis hit Slovenia hard leading to a recession in 2009. It also exposed high debts levels in domestic companies which led to a banking crisis and another recession in 2012-13. Growth returned after the government recapitalised the banking system, increased public investment (with EU funds), and exports increased.
Trade agreement information for Slovenia
Does Slovenia belong to any economic unions or free trade areas?
Member of the European Union (EU) since 01/05/2004
Other members:
Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden
Which trade deals does Slovenia have through its membership of the EU?
EU - Andorra Customs Union (from 01/01/1991)
European Single Market (SM) (from 01/01/1993)
EU - Sri-Lanka Co-operation and Partnership Agreement (from 01/04/1995)
EU - Turkey Customs Union (from 31/12/1995)
EU - Faroe Islands Agreement (from 01/01/1997)
EU - Palestinian Authority Interim Association Agreement (from 01/07/1997)
EU - Tunisia Association Agreement (from 01/03/1998)
EU - Armenia Partnership and Cooperation Agreement (from 09/09/1999)
EU - Morocco Association Agreement (from 01/03/2000)
EU - Israel Association Agreement (from 01/06/2000)
EU - Mexico Global Agreement (from 01/10/2000)
EU - San Marino Customs Union (from 01/04/2002)
EU - Jordan Association Agreement (from 01/05/2002)
EU - North Macedonia Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2004)
EU - Pakistan Co-operation agreement (from 29/04/2004)
EU - Egypt Association Agreement (from 01/06/2004)
EU - Chile Association Agreement and Additional Protocol (from 01/03/2005)
EU - Algeria Association Agreement (from 01/09/2005)
EU - Lebanon Association Agreement (from 01/04/2006)
EU - Albania Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2009)
EU - Montenegro Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/05/2010)
EU - Central America Association Agreement (from 01/08/2013)
EU - Serbia Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/09/2013)
EU - Bosnia and Herzegovina Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/06/2015)
EU - South Korea Free Trade Agreement (from 01/07/2015)
EU - Kosovo Stabilisation and Association Agreement (from 01/04/2016)
EU - Georgia Association Agreement (from 01/07/2016)
EU - Moldova Association Agreement (from 01/07/2016)
EU - Canada Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) (from 21/09/2017)
EU - Eswatini (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Lesotho (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Mozambique (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Namibia (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - South Africa Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Botswana (SADC) Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
EU - Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (from 01/02/2019)
EU - UK Withdrawal Agreement Transition Period (from 01/02/2020)
What bilateral trade deals are there between Slovenia and other countries and economic unions?
None
Trade between Slovenia and the United Kingdom
Source: UK Office for National Statistics, October 2019.
Contains public sector information licensed under the Open Government Licence v3.0.
 Its population in 2018 was 2,081,260 [1]
Its population in 2018 was 2,081,260 [1]
 In 2015, 20.88% of its total energy
In 2015, 20.88% of its total energy
consumption was renewable [2]
 In 2018, its GDP grew by 4.49% [2]
In 2018, its GDP grew by 4.49% [2]
 In 2018 it had a positive Current
In 2018 it had a positive Current
Account Balance of US$bn3.47 [3]
 Its unemployment rate in 2018 was 5.77% [3]
Its unemployment rate in 2018 was 5.77% [3]
 Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
GDP) in 2016 was 2.00% [2]
Data sources