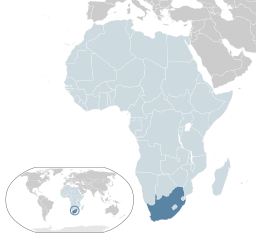
CFI Data on South Africa
South Africa is the 32nd largest economy in the world by nominal GDP (2018) and is the second largest economy in Africa (after Nigeria). It is rich in minerals including diamonds, gold, and platinum metals (91 percent of global reserves). It has well-developed financial, legal, communications, energy, and transport sectors; and has the largest stock market in Africa. GDP per capita is $6,374 USD. It is the only African member of the G20. Services was the largest sector in 2018 (61 percent), followed by manufacturing (11.8 percent), and agriculture 2 percent. Its largest export sectors in 2017 were precious metals and stones (24 percent) minerals (19.4 percent), services (12.9 percent), agriculture (10.4 percent), metals (9.2 percent), and vehicles (8.7 percent). The largest individual exports were gold (14 percent), travel and tourism (7.2 percent), platinum (6 percent), cars (5.3 percent), coal (4.7 percent), and iron ore (4.4 percent). Its largest export partners were China (18.7 percent), USA (6.8 percent), Germany (6 percent), UK (5.6 percent), and India (5.3 percent). Its largest goods imports were crude oil (7.3 percent), refined oil (5 percent), cars (4.6 percent), and car parts (3.8 percent). The discovery of diamonds and gold in the late 1800s revolutionised the economy, in addition to income it brought international investment which furthered development. During the first half of the 20th century the economy grew as the government encouraged the development of manufacturing and farming through tariffs, incentives, and state corporations. But by the 1970s the economy was in decline as mining output reduced, marginal productivity gains from investment decreased, and population growth outstripped economic growth. Social tensions from apartheid and increasing international sanctions also had their toll. Post-apartheid, the government has sought to encourage private investment through deregulation, privatisation, and fiscal discipline. In 2013, the government began implementing the "National Development Plan 2030" with the aim of reducing poverty and inequality. While investment and growth have been slower than expected, the foundation for increased future growth has been laid through necessary structural reforms.
Trade agreement information for South Africa
Does South Africa belong to any economic unions or free trade areas?
Member of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) since 01/04/2019
Other members:
Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Chad, Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Djibouti, Egypt, Equatorial Guinea, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Mali, Mauritania, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Togo, Uganda, Western Sahara, Zimbabwe
Member of the Southern African Customs Union (SACU) since 01/01/1910
Other members:
Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, Namibia
Which trade deals does South Africa have through its membership of the SACU?
SACU - EFTA free trade agreement (from 01/07/2006)
MERCOSUR - SACU partial scope agreement (from 01/04/2016)
UK - SACU+M trade agreement (from 01/01/2021)
What bilateral trade deals are there between South Africa and other countries and economic unions?
Southern African Development Community (from 01/09/2000)
EU - South Africa Economic Partnership Agreement (from 05/02/2018)
Implementation dates might vary according to the date of the United Kindom's exit from the European UnionTrade between South Africa and the United Kingdom
Source: UK Office for National Statistics, October 2019.
Contains public sector information licensed under the Open Government Licence v3.0.
 Its population in 2018 was 57,398,421 [1]
Its population in 2018 was 57,398,421 [1]
 In 2015, 17.15% of its total energy
In 2015, 17.15% of its total energy
consumption was renewable [2]
 In 2018, its GDP grew by 0.62% [2]
In 2018, its GDP grew by 0.62% [2]
 In 2018 it had a negative Current
In 2018 it had a negative Current
Account Balance of US$bn12.09 [3]
 Its unemployment rate in 2018 was 27.93% [3]
Its unemployment rate in 2018 was 27.93% [3]
 Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
Its Expenditure on R&D (as a percentage of
GDP) in 2015 was 0.80% [2]
 A Big Mac will set you back the
A Big Mac will set you back the
local equivalent of US$2.24 [4]
Data sources